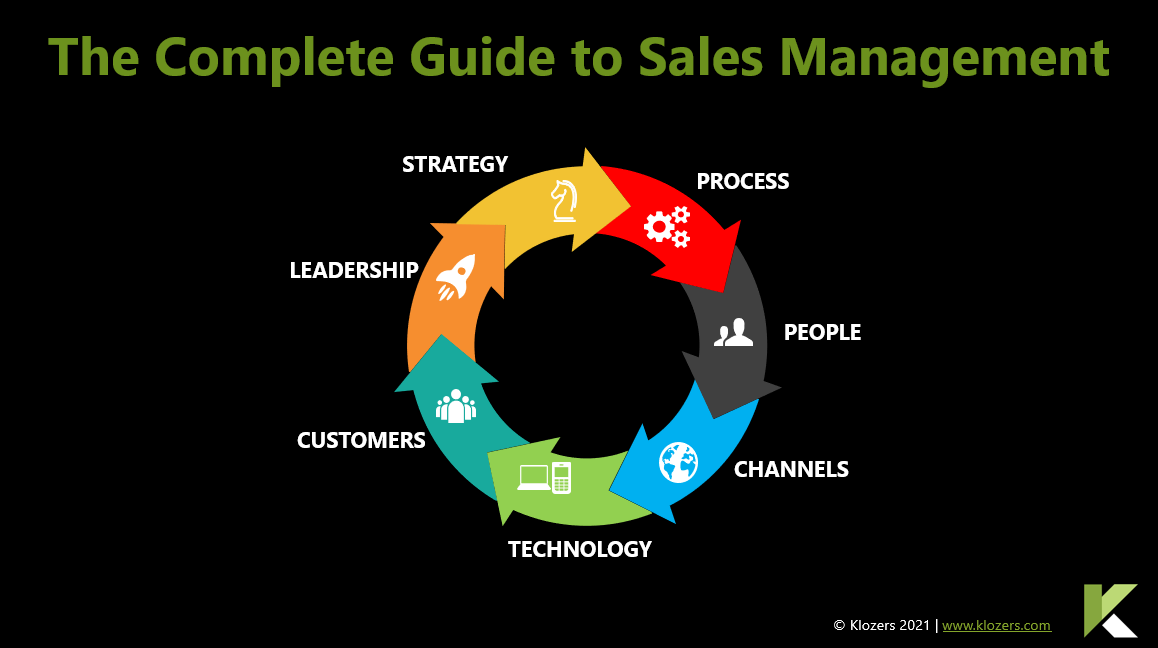
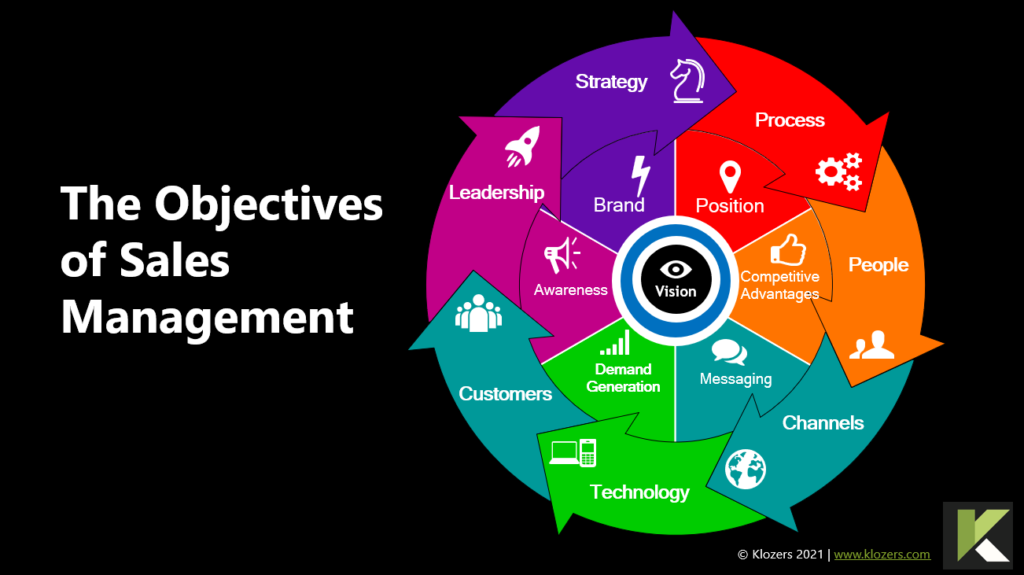
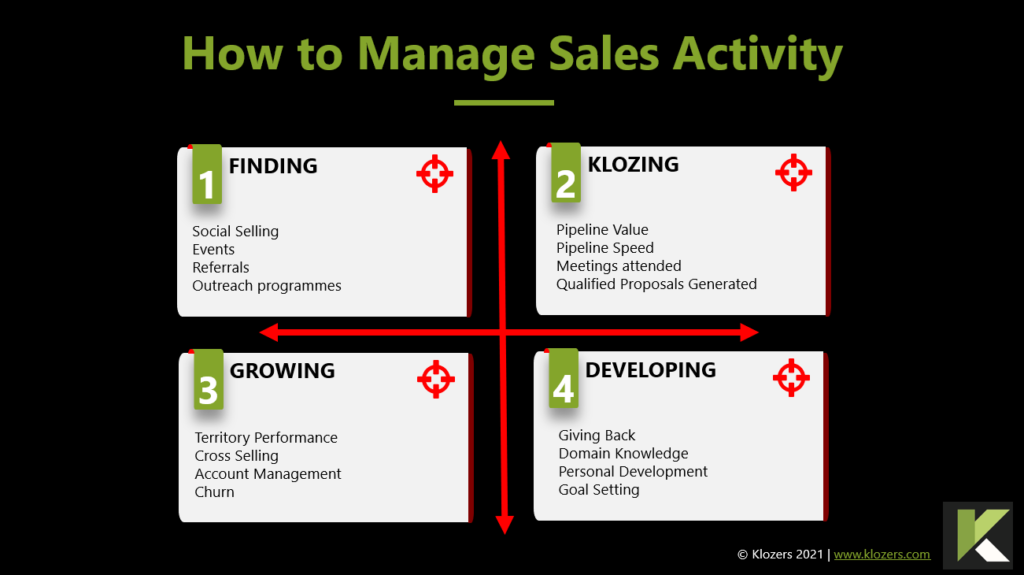
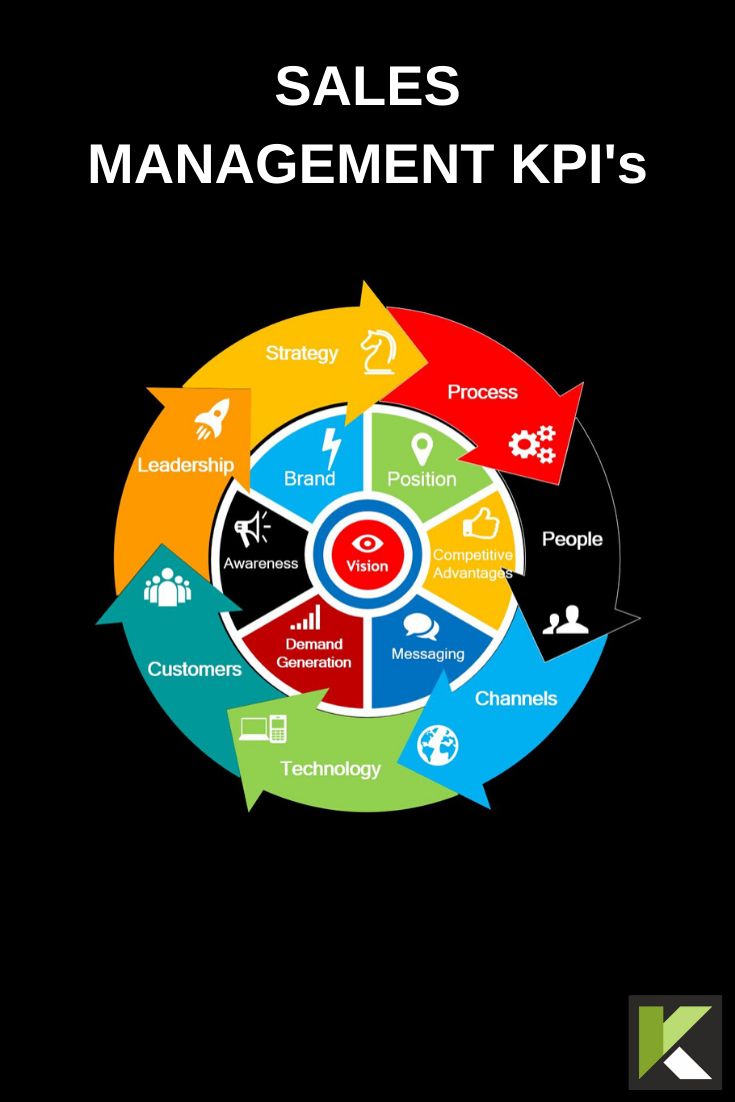
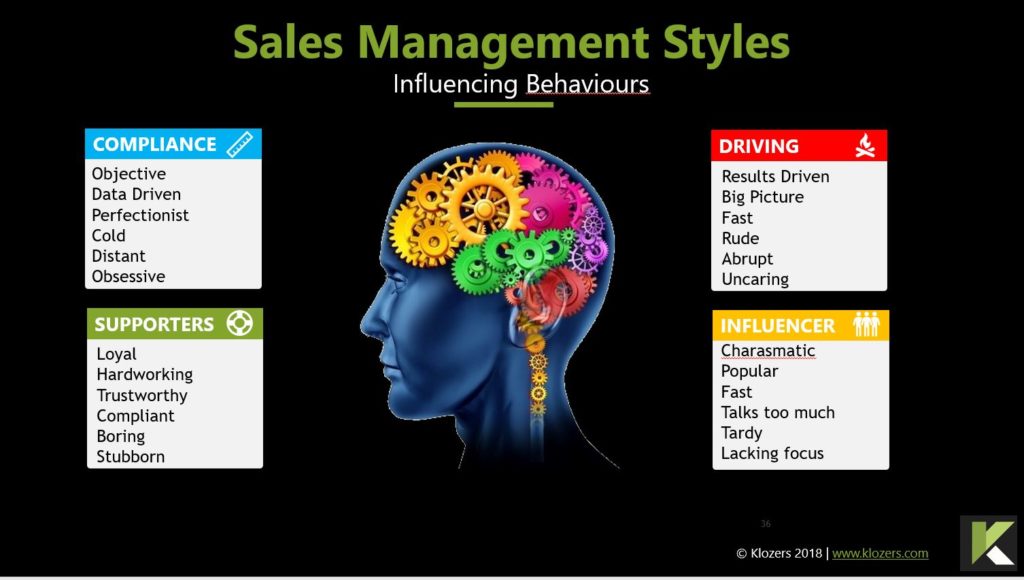
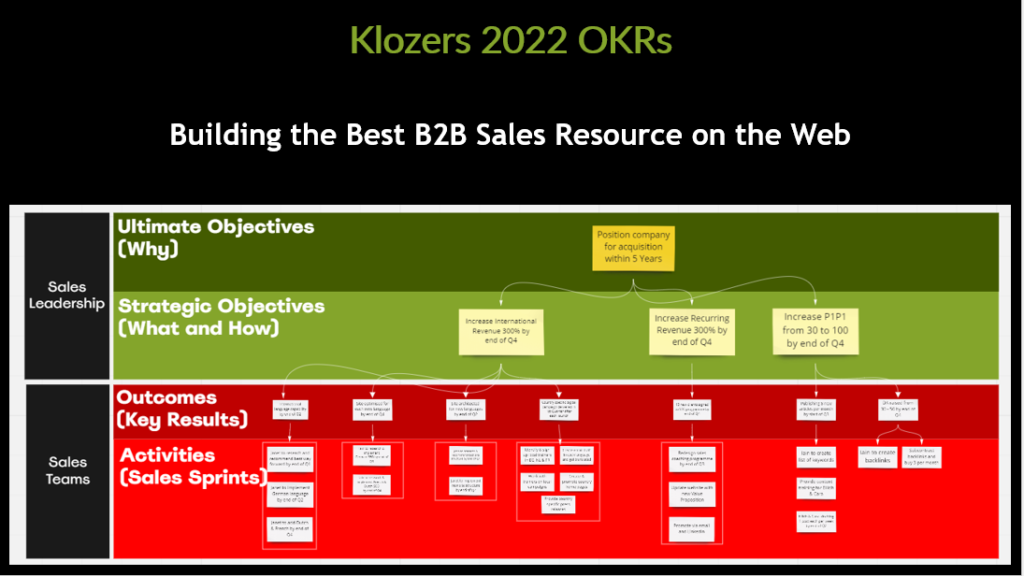
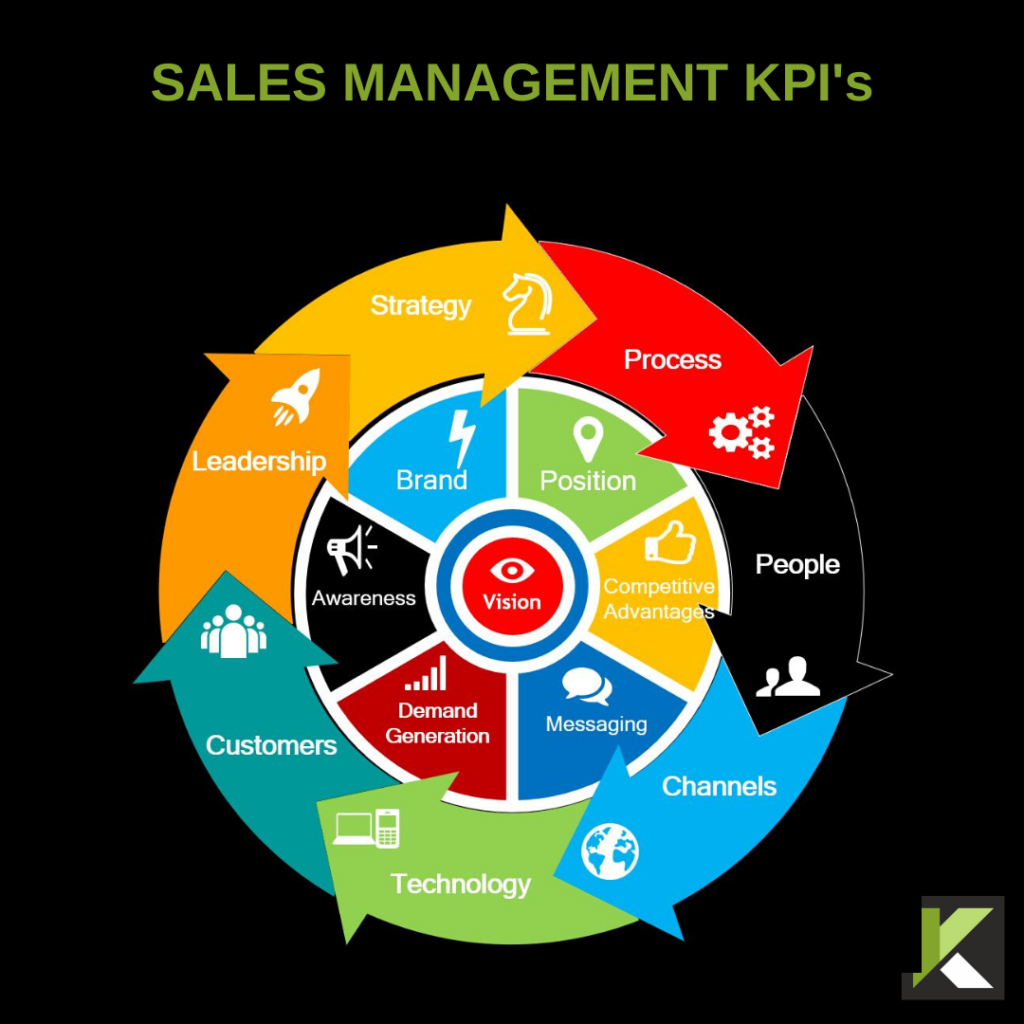
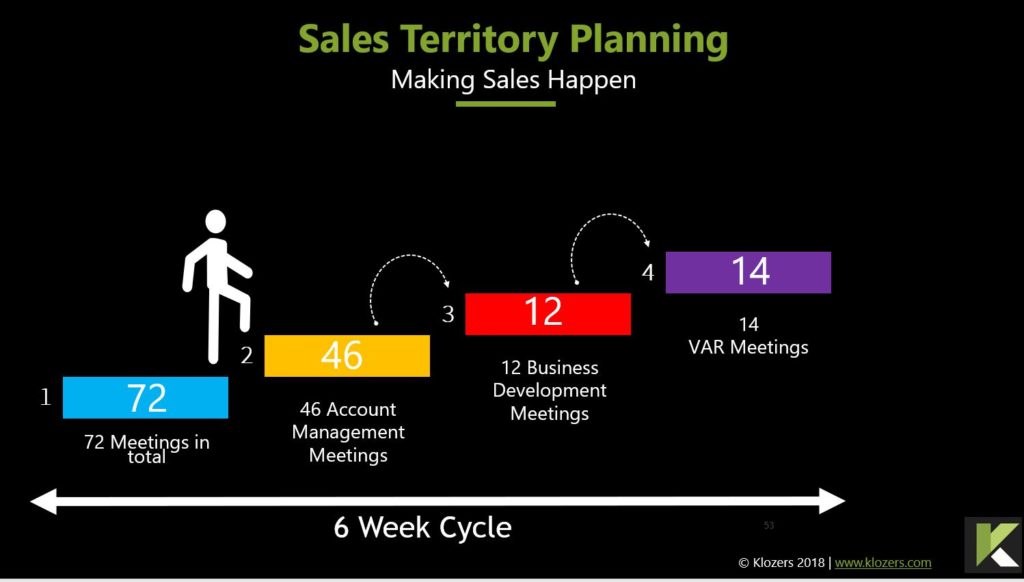
Sales Teams with Sales Playbooks are 33% more likely to be high performers with win rates exceeding 50%

What is a Playbook in Sales
A playbook in Sales is a single repository that contains all the information, tools, templates, content, media, training and coaching that Salespeople require to execute their role successfully. The most common use of playbooks are for onboarding new salespeople, however, they are great for documenting your sales process and coaching salespeople.
What makes a good Sales Playbook?
A good sales playbook will help onboard new salespeople and get them to generate revenue as fast as possible. Playbooks help existing sales reps follow best practice, a proven sales process , develop their sales skills and behaviours and improve their productivity.
Join the next webinar for step by step instructions on how you can customise this playbook template for your business
Please note: The B2B Sales Playbook is built in the paid version of Microsoft OneNote that is included with Microsoft Office 365.
The Playbook will not open or load in the free version of OneNote.
Grab your template here:
1. Sales Playbook Framework
We’ve included our most popular sales tools and templates to provide you with the best sales playbook in the world and it’s 100% free.
Our sales playbook template is built inside Microsoft OneNote so it’s completely customisable to the needs of your own organisation.
Built with over 90 pages in 12 different sections this Playbook has everything you will ever need to know to help your Sales Team become more productive and proficient.
We recommend that you host the playbook inside a Channel in Microsoft Teams in order that sales and marketing teams working remotely can also access the document.
2. SaaS Sales Playbook Outline
SaaS playbooks or Inside Sales Playbooks are often different because SaaS sales can have a different sales process and structure, but either way we’ve got you covered.
For example, many SaaS companies have teams of Sales Development Reps (SDR’s) who are responsible for lead generation and the initial sales qualification process.
These B2B SaaS companies are scaling and Sales Playbooks form a vital role in recording, tracking and developing the sales function within the business as well as onboarding new sales team members.
In addition, the playbooks act as a simple but very effective sales enablement solution, helping them learn and implement best practice in sales while increasing productivity and performance via sales coaching and training.
Your sales playbook is the home for everything your sales and marketing teams need to be successful, From templates for buyer personas, buyer pain points, cold email templates, documenting the buyer’s journey, sales processes and use cases we’ve got you covered.
Playbooks are especially important for new hires who need to get up to speed and delivering as quickly as possible. Our template is the quickest way to get started creating your sales playbook and populating it with relevant content for your own sales team.
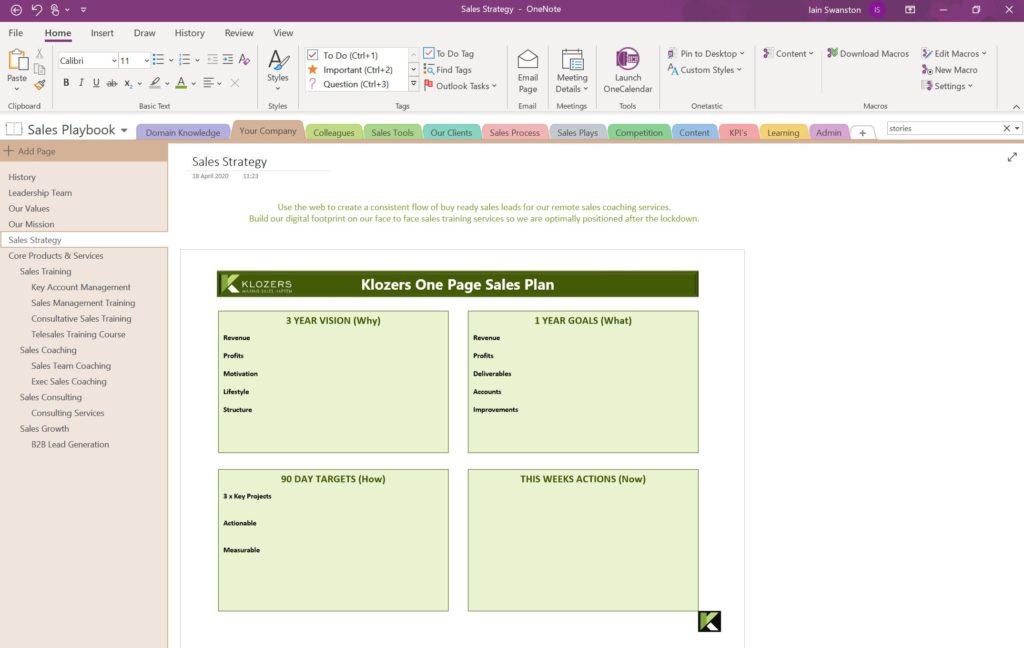
3. Sales Playbook Benefits
- Single Location: Playbooks provide a single location for everything a B2B Sales Reps needs to know in order to do their job successfully. Rather than having pieces of information scattered across different file locations, and in different departments which are difficult and time consuming to find, your Sales Playbook keeps everything in one easy to find location.
- Commonality: Sales Playbooks provide a common sales language that your sales and marketing teams can understand and follow.
- Continuous improvement: Digital Playbooks provide a living, working document that can be continuously updated to retain relevancy.
- Standardised Sales Process: Playbooks help salespeople follow the company’s proven sales process and buyer’s journey rather than having every sales rep following a different process.
- Best Practice: Sales Playbooks provide a location to document and report on the companys’ best practices in selling for others to learn and follow.
- Sales Coaching & Training: Sales playbooks provide a location to document and report on the learning & development plans for B2B sales reps. A good playbook improves the Sales Reps productivity and performance.
7. Save Time: Every leader in a SaaS company is time poor and having access to an instant knowledge base of sales content provides a solid foundation as you are building your team.
8. Building an Asset: As you begin to customise your sales playbook to meet your own strategy and methodology you can build in your own organisations KPIs, material, call scripts and content so it becomes a long term asset for the business.
9. Step by Step Guide: Your sales playbook provides a step by step guide on how your organisation goes to market. It covers everything from buyer personas, how to hire and onboard new reps, to KPI’s ROI, Performance management, proposals, channels, planning and strategy. It’s a single point of reference for everything in sales.
4. Sales Playbook Best Practices
1. Customisation – no two SaaS companies are the same so while it’s great to start with a framework, it’s important to customise the content of the playbook to match the needs of your organisation. Think of our playbook as a template to give you a head start on creating your own.
2. Updating – sales is a fast paced environment that is constantly changing and your sales playbook needs to be a living working document. Playbooks should be updated regularly and reviewed completely every six months.
3. Ownership – have a limited number of playbook owners with admin rights to stop anyone and everyone from editing the document. In OneNote this can be achieved by password protecting sections and pages. Improvements and additions can be fed back to the administrators on an ad-hoc basis or at Sales Meetings.
4. Engagement – playbooks have no impact on Sales unless they are used. Sales Managers must hold Sales Reps accountable to using and following the playbooks. “51% of reps attain quota at firms using a Sales Playbook, compared to 40% at firms who don’t have a Sales Playbook.” Aberdeen Group
5. Content – In addition to being relevant content should be easy to consume and engaging. Avoid massive PowerPoint decks with generic messaging. Use multimedia and a mixture of content types where possible.
6. Access – Sales Playbooks should be Cloud based however having access to them offline may be critical for some Reps, in which case the Playbooks should be downloadable but with restrictions on editing.
5. Sales Playbook Content
Your copy of the best Sales Playbook in the World contains:
5.1 DOMAIN KNOWLEDGE
This is where you can store information on your industry like statistics, trends and market intelligence. You can track and follow Industry Thought Leaders, top industry publications and Industry Bodies and Organisations so your teams are always up to date.
5.2 YOUR COMPANY
In this section you can provide details on your company’s History, Mission and Values. This is also where you would place your Sales Strategy and Sales Plan so every team member knows the “Why” behind what you do, and can align their sales behaviours with the Sales Plan. Lastly in this section we record all the companies products and services.
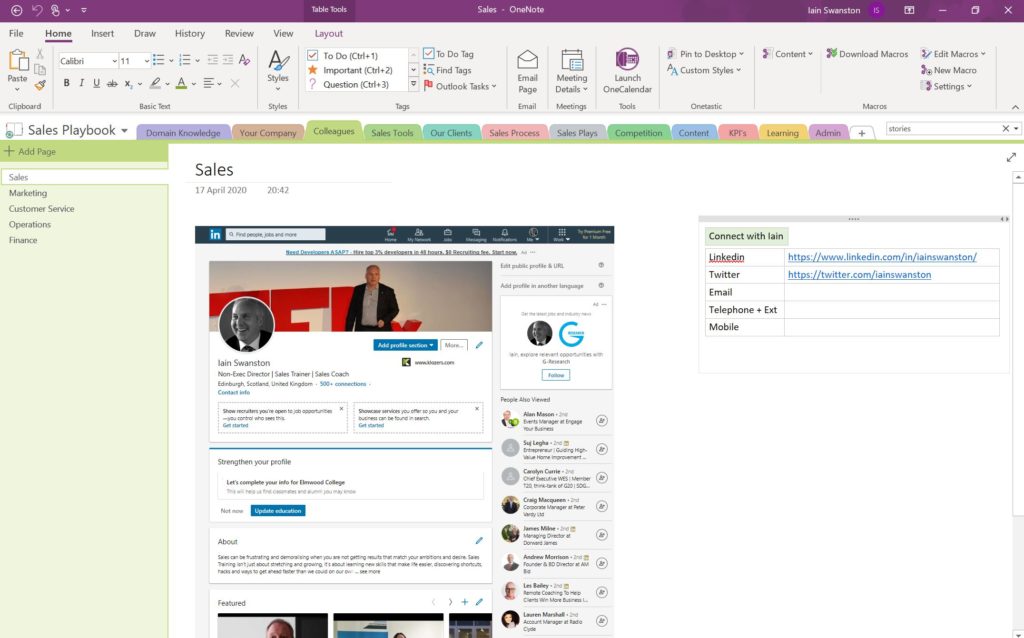
5.3 YOUR COLLEAGUES
When you join a new company and you don’t know anyone the first few weeks can be quite intimidating. This section contains an internal directory in order that new team members can quickly identify and connect with any colleague including those outside the sales department.
5.4 SALES TOOLS
The modern B2B sales team uses at least six sales tools and in addition to finding login details quickly salespeople need quick access to Training, Knowledge Bases and Support details. Some examples of Sales Tools are MS Teams, CRM, Office 365, Digital Signing, Cloud Storage, LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram, Marketing Automation, Email Automation, Email Finders, Video Email Apps, Survey Apps and Training programmes.
5.5 OUR CLIENTS
This section is where you can store information of your clients. These are typically examples of clients/buyers that fit your sales prospect profiles, common pain points, clients who provide good case studies, testimonials, channel partners or strategic accounts.
5.6 SALES PROCESS
It’s important that Reps have and follow a proven Sales Process. This process provides a track for the salespeople to follow which is repeatable and measurable. We have also included an example of our Qualifying template which you can customise to meet your own needs.
5.7 SALES PLAYS
Sales plays are where we document our sales messaging and structure for controlling the sales conversation with a buyer. They include templates for what we call a Door Opener which is similar to an Elevator pitch. There are also sections for buyer personas, pain points, how to deal with prospects Stalls & Objections, How to deliver product Demos, Pricing, Proposals, Sales Stories and Customer Meeting Notes.
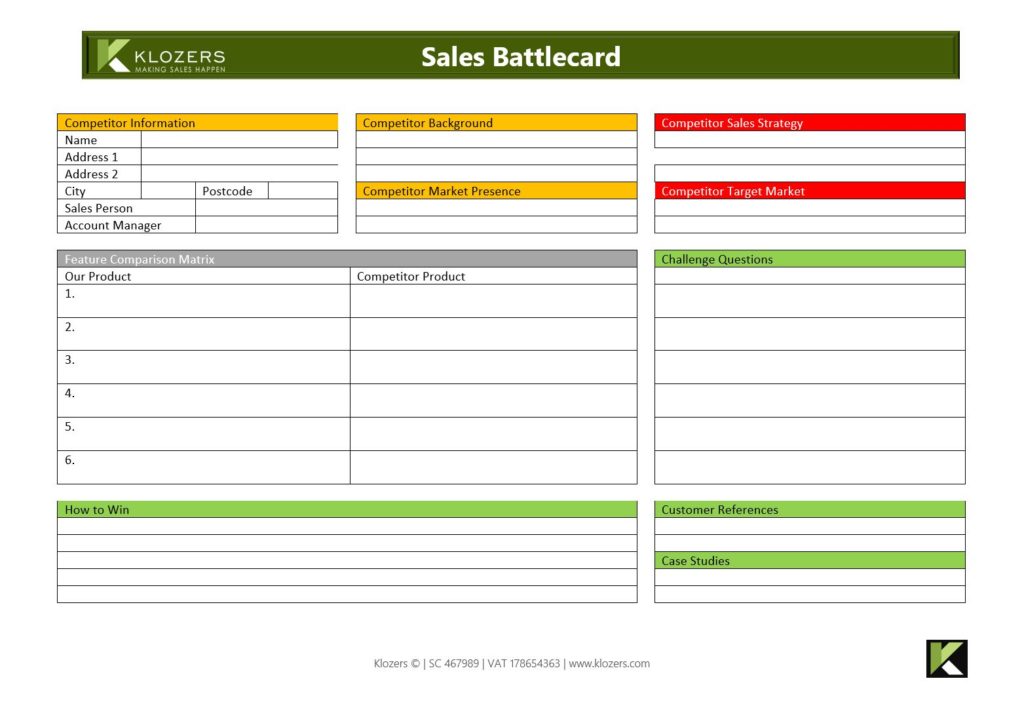
5.8 COMPETITION
This is where you can store information and intelligence on your competitors. We are great fans of Sales Battlecards which you can use to win deals against your competition. The Battlecards help you steer the buyer conversation to the areas that favour your solution the most and make it more difficult for your competitors to compete. In short this shows you how to move the goals posts in the middle of the sales process to sabotage your competitors bid.
5.9 CONTENT
No more searching for files, flyers, technical specifications, case studies, testimonials and pricing sheets. Everything is stored inside this OneNote section in your sales playbook.
5.10 KPI’S
Every Sales Rep needs to know their numbers and what are the Key Deliverables for their role. We have listed all the KPI’s you will need for you to choose from and then create your own Sales Scorecards to manage Sales Reps.
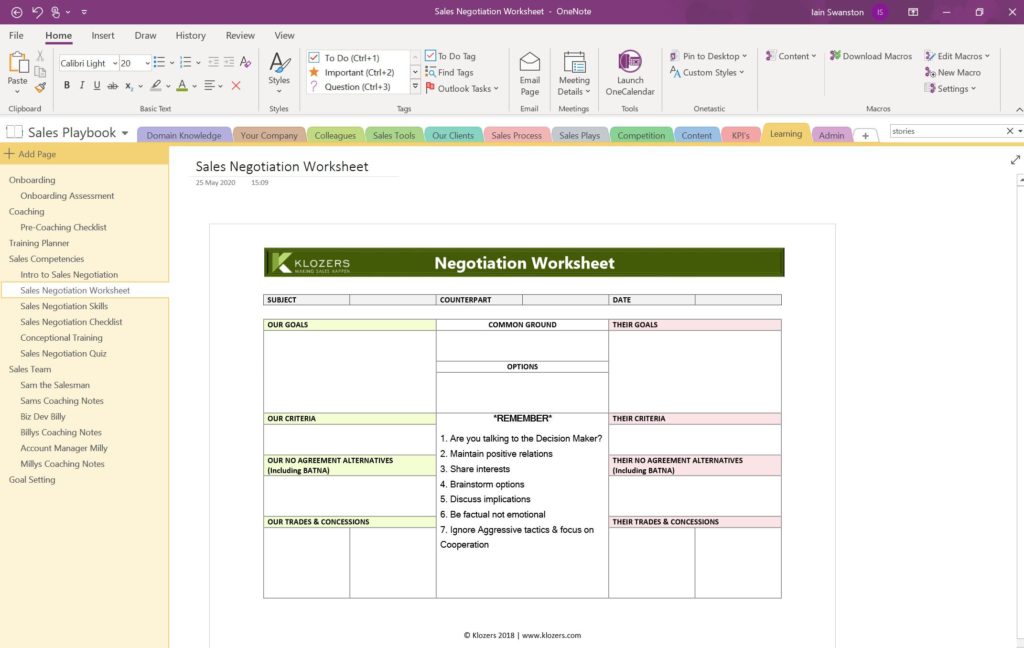
5.11 LEARNING
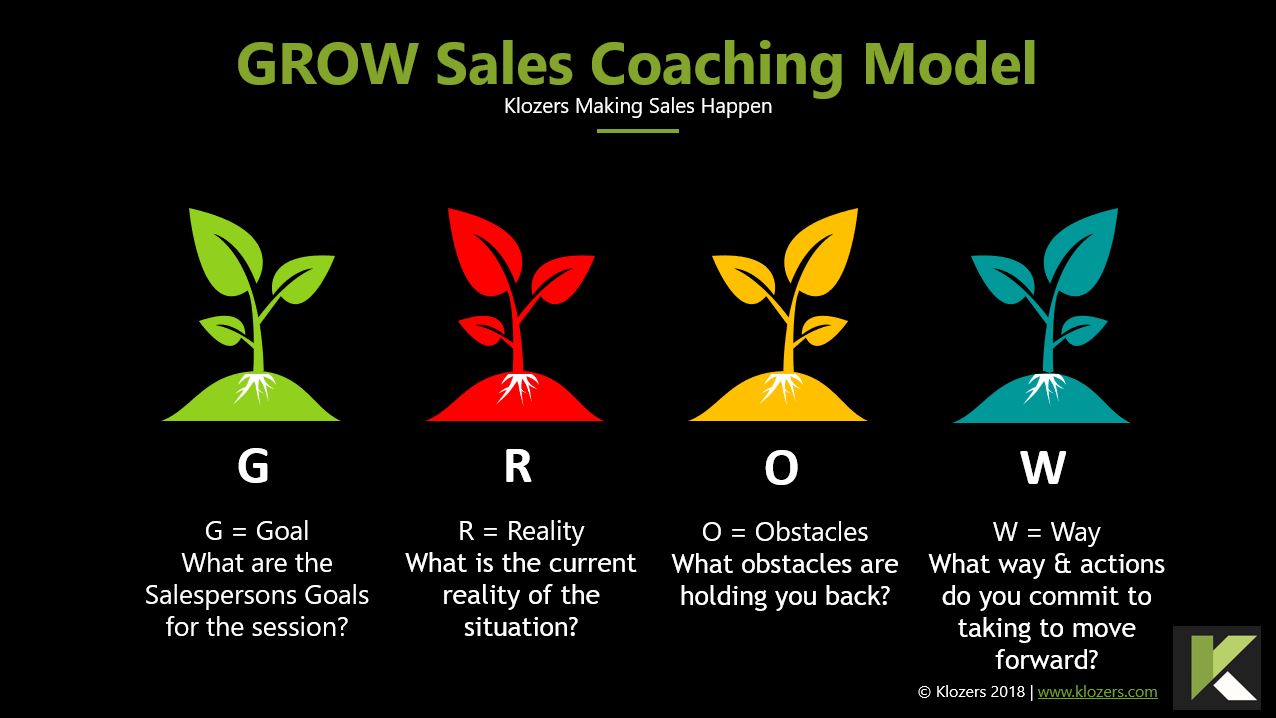
Learning is your library for Onboarding Plans, Sales Coaching Playbooks, Training Planners, Personal Learning Plans, Sales Coaching Notes, Goal Setting and experiential learning and simulations.
5.12 ADMIN
The very last section is our Admin section. In here we store Team Meeting notes, Compensation & Commission, Expenses and a Time Management Tracker.
6. Sales Coaching Playbook
As a sales training and coaching company we use Sales Playbooks for training and sales coaching probably more than any other business. Playbooks are a great place to include:
- Onboard Plans for new Salespeople
- Personal Learning Plans
- Sales Coaching Plans
- One to One Sales Coaching Notes
- Training Plans
- Skills Based Training Modules
- Activity Based training Modules
- Product Training
7. Sales Messaging Playbook
Sales Messaging is an often overlooked and undervalued area of sales, however when you lose business to a competitor it means that someone else is either saying or doing something better than you.
In sales, we have little to no control of the product, but we have 100% ownership of our messaging.
Robert Cialdinis best seller Influence is a testament to this and a great read for anyone in sales.
We call our Sales Messaging our Sales Plays and we have a whole chapter in the playbook dedicated to this.
Sales Messaging – our Sales Plays should include every possible part of the Sales Conversation that a Salespeople will have as they walk a prospect/buyer through the sales process.
In addition, our Playbook includes templates for creating your Perfect Prospect Profile / buyer personas to make sure your messaging matches with your prospect/buyer in every way.
8. Sales Playbook Download
Join the next webinar for step by step instructions on how you can customise this playbook template for your business
Please note: The B2B Sales Playbook is built in the paid version of Microsoft OneNote that is included with Microsoft Office 365.
The Playbook will not open or load in the free version of OneNote.